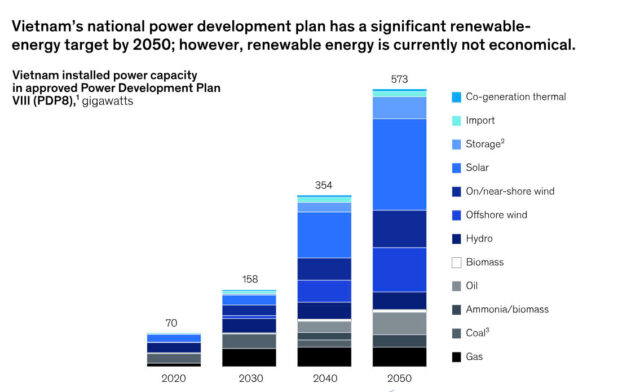
Vietnam’s long-awaited Power Development Plan VIII (PDP8) has recently been approved, setting ambitious renewable-energy goals for 2030—similar to the recommendations for Vietnam to embrace renewables set out in our 2019 article, “Exploring an alternative pathway for Vietnam’s energy future.” These goals are focused on boosting renewable energy while reducing the country’s reliance on coal. This presents Vietnam with a conundrum: its renewable-energy projects are not consistently bankable at present, held back by regulations and the market.
However, current market conditions present the country’s energy sector with a unique opportunity. Many manufacturers are avoiding investing solely in China by diversifying into neighboring countries to mitigate geopolitical risk, including into Vietnam. To support this trend of incoming foreign direct investment (FDI), Vietnam could deploy more renewables to meet commercial and industrial (C&I) customers’ increasing demand for renewables. If it can seize this opportunity and successfully address the challenges that arise, Vietnam has the potential to become a regional champion for both installed renewable capacity and sustainable manufacturing.
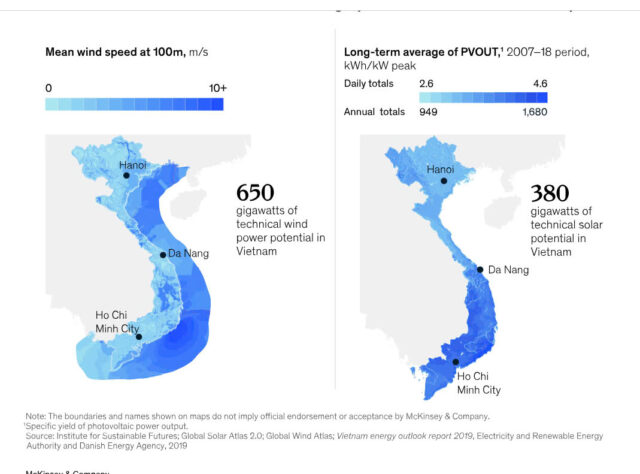
Yet, after an initial wave of (mostly solar) projects driven by favorable feed-in tariffs (FiTs), current renewable-energy projects are no longer consistently economically viable. Unless this situation changes, Vietnam’s net-zero ambitions—as well as the PDP8’s goals—are at risk, with market and regulatory constraints preventing this potential from being realized (Exhibit 2). Consider also that Vietnam’s neighbors might develop renewable energy faster, attracting international 100 percent renewable-energy (RE100) manufacturers at Vietnam’s expense. The time to ramp up renewable-energy production is now—for the business opportunity as well as the country’s sustainability.